Operational Resilience in Banking: Unbreakable Shield
Shambhavi Singh
November 21, 2025
Regulatory activities are evolving and going through a shift to emphasize risks occurring from the introduction of digital tools and technology in banks and financial institutions. This is becoming more visible as banks are facing competitive pressure from all sides to switch to a digitally aided business model. This digital model will help in managing costs and being up-to-date with customer demands, needs, and feedback. As digitalization becomes the new norm in the banking sector, new vulnerabilities come along too. These new vulnerabilities could trigger the urgency to achieve operational resilience in banking to minimize disruptions in operations.
At this point the banking sector stands at a crossroads. The rapid & unprecedented growth of digitalization makes the industry confront a new wave of risks and threats. Regulatory authorities across the world are also shifting their emphasis from traditional financial risk to the new era threats created by advanced technologies, digital products, cloud services, AI systems, and interconnected third-party environments.
In today’s hyper-digital world, banks and financial institutions are facing competitive pressure from all directions. Customers expect seamless digital experiences. FinTechs continue to disrupt long-standing banking norms. Operational costs are rising. To stay relevant, banks are rapidly transitioning to digitally enabled business models that promise agility, efficiency, and customer delight With this shift towards digitalization comes an equally powerful challenge called digital fragility.
New technologies expose the industry to new threats. A single system failure, cyber incident, supplier outage, or data breach can bring operations to a halt, impacting customer trust, damaging reputation, attracting regulatory penalties, and causing severe financial losses.
This growing complexity has sparked a global urgency for financial institutions to build operational resilience.
What Is Operational Resilience?
Operational Resilience is the ability of enterprises to avoid, act, recuperate, and learn from operational disruptions. Any resilient business protects its core critical functions from a disruption. It is the ability to prevent, withstand, respond to, and recover from disruptions while continuing to deliver critical services at the same time. The goal is not merely to restore operations after an incident but to ensure continuity throughout the disruption.
Unlike traditional risk management that focuses on identifying and mitigating risks, operational resilience expands the scope to:
- Forecasting incidents before they happen
- Withstanding the disruption
- Minimizing customer dissatisfaction
- Swift and quick operations recovery
It integrates cybersecurity, business continuity, disaster recovery, third-party risk management, technology governance, and incident response into one cohesive framework.
Why Operational Resilience Is Now a Strategic Priority in Banking
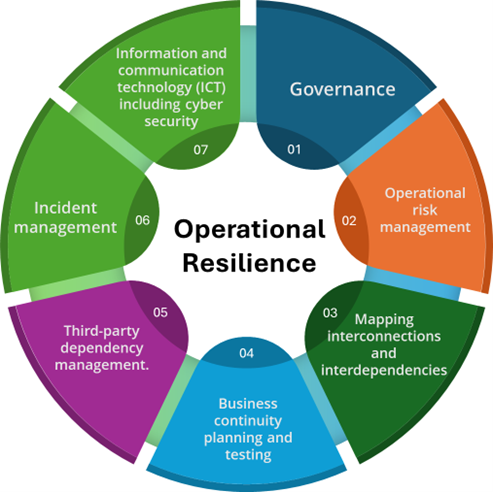
- Unprecedented Digitalization
Banks are moving aggressively toward online banking, cloud computing, open APIs, mobile payments, and AI-driven services.
While these innovations offer extraordinary advantages, they also bring along risks. Risks like increased cyberattacks, over-dependence on third-party technology vendors, interconnected systems prone to cascading failures, cloud outages impacting thousands of customers simultaneously, and sensitive data at risk due to integration gaps.
In short, the more digital a bank becomes, the more resilient it must be. With great efficiency comes great fragility too. - Strict Guidelines by Regulatory Bodies
Operational resilience is no longer just the best preferred practice; rather, it’s a regulatory mandate.
Regulators like the RBI, PRA (UK), MAS (Singapore), OCC (USA), and EBA (Europe) are issuing strict guidelines that require banks to identify important business services and define impact tolerance levels. They need businesses to map dependencies, conduct scenario testing, strengthen ICT (Information & Communication Technology) frameworks, and ensure third-party accountability. - Uncountable Cyber Threats
Cyber criminals are now leveraging AI, automation, and deep social engineering to launch more targeted attacks such as ransomware, phishing 2.0, multi-layered DDoS attacks, supply-chain attacks, etc. A single cyber incident can cause prolonged downtime, data compromise, lost customer trust, and penalties. Operational resilience ensures banks have layered defenses, fast response mechanisms, and strong recovery capabilities. - Increasing Customer Expectations
Today’s financial customers demand uninterrupted support, real-time transactions, instant payments, and a seamless experience across channels. Any disruption, be it big or small, can lead to customer loss. Operational resilience ensures that customer support continuity remains intact even under extreme pressure. - Third-Party Dependency
Banks now rely on various third-party applications for cloud services, digital KYC, payment gateways, data centers, AI analytics, etc. These third-party relationships expand the risk landscape significantly. Operational resilience mandates banks to ensure vendor continuity, legally enforceable SLAs, and backup strategies for critical suppliers.
Key Regulations Strengthening Operational Resilience in Banking
- RBI’s Increased Focus on IT & Cybersecurity
RBI has released detailed frameworks on IT governance, cyber incident reporting, business continuity planning, outsourcing of digital services, and data protection. These highlight the need for resilience across the banking ecosystem. - DORA (Digital Operational Resilience Act) in EU
DORA mandates classification of risks, ICT incident reporting, resilience testing, and third-party oversight. Banks that operate internationally must comply with it. - UK Prudential Regulation Authority (PRA) Operational Resilience Framework
It requires banks to identify important business services, set impact tolerance levels, test severe but plausible scenarios, and ensure board accountability. - Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS)
Basel’s guidelines outline global expectations for risk governance, ICT continuity, capacity management, and resilience metrics. These guidelines signal a global shift towards proactive resilience.
Building Operational Resilience in Banking: A Step-By-Step Guide
Below is a step-by-step framework banks can adopt to build a strong resilience posture:
Step 1: Identify Critical Business Services
The first step is to determine which services, if disrupted, would cause severe customer impact, financial loss, or regulatory non-compliance. These services can be classified as core critical services such as core banking, payment systems, loan processing, mobile banking, ATM operations, etc.
Step 2: Map Dependencies
The next important step would be to map the dependency of such services. Each service depends on various factors such as applications, infrastructure, vendors, people and facilities. Mapping the dependency of the services provides clear visibility into pain points and vulnerabilities.
Step 3: Analyse Impact Tolerance
The third step boils down to defining the maximum acceptable outage time before customer trust dwindles or financial harm occurs. For instance, an ATM failure must be restored within an hour.
Step 4: Scenario Testings
Simulate cyberattacks, data center outages, cloud downtime, payment system failures, and third-party breaches. These tests would reveal blind spots and drive improvements in the system.
Step 5: Strengthen Risk Controls
Implement automated monitoring tools, multi-layered security, redundant systems, vendor audit mechanisms, and robust SLAs with penalties.
Step 6: Build Resilience
Operational resilience is not an IT project. It is an organizational mindset.
Banks must train teams, enforce governance, align leadership, promote accountability, and embed resilience in decision-making.
Step 7: Continuous Monitoring & Improvement
Resilience is not static. Banks must regularly review impact tolerances, update business continuity plans, reassess supplier risks, enhance cyber defenses, and refine incident response playbooks.
The Business Value of Operational Resilience in Banking
Operational resilience in banking is more than just about compliance. It is a strategic advantage.
Banks that invest in maintaining their resilience lead to:
- Higher customer trust
- Reduced downtime costs
- Stronger regulatory compliance
- Competitive differentiation
- Increased investor confidence
Conclusion
The banking world is becoming increasingly digital, interconnected, and vulnerable to disruption. From cyber threats to system outages to third-party failures, risks are multiplying faster than ever.
To thrive in this complex landscape, banks must evolve from reactive risk management to proactive operational resilience. A resilient bank is not one that avoids disruptions, but one that can withstand them, adapt, recover, and continue delivering critical services without missing a beat.
As technology advances and risks grow, building operational resilience is no longer optional; it’s the foundation of future-ready, unbreakable banks.
Written by
Shambhavi Singh is a Marketing Executive at Ascent Risk & Resilience, where she contributes to brand communication, content strategy, and digital storytelling across the organization’s risk and resilience solutions. With a background spanning content writing, voice-over artistry, anchoring, public speaking, and social impact, she brings both creativity and clarity to every message she crafts.
Shambhavi’s passion for communication started early in her hometown of Varanasi, where her curiosity for culture and heritage shaped her worldview. A natural storyteller and confident speaker, she has built a strong presence as a social media writer and continues to use her voice to inform, inspire, and engage audiences.
Driven by a blend of will and skill, she is committed to building meaningful connections, leading with empathy, and contributing to initiatives that create positive change. A social worker at heart and a marketer by profession, Shambhavi combines creativity, purpose, and leadership in everything she does.